Porcelain Crowns vs Zirconia Crowns: Key Differences Explained
Dental crowns play a crucial role in restoring damaged or weakened teeth. Thanks to advancements in dental technology, patients now have access to a wider range of materials tailored to their specific needs and aesthetic preferences. Among the most commonly used options are porcelain crowns vs zirconia crowns.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at these two popular crown types, comparing their key features, strengths, and limitations, to help both dental professionals and patients make informed decisions based on durability, appearance, biocompatibility, and clinical application.
What are porcelain crowns vs Zirconia crowns?
Understanding Porcelain Crowns
A porcelain crown is a dental restoration that covers a damaged natural tooth by being placed over it to restore its shape, size, and function. These crowns are made from dental porcelain—a ceramic material known for its lifelike translucency and color. One of the main appeals of porcelain crowns lies in their ability to seamlessly blend with surrounding teeth, thanks to their enamel-like translucency. Porcelain can be used on its own or fused to a metal substructure (PFM) or a zirconia core (PFZ).
Porcelain crowns are commonly indicated for anterior teeth, where esthetics are especially important. They can be color-matched to surrounding teeth for a natural-looking smile that enhances patient satisfaction.
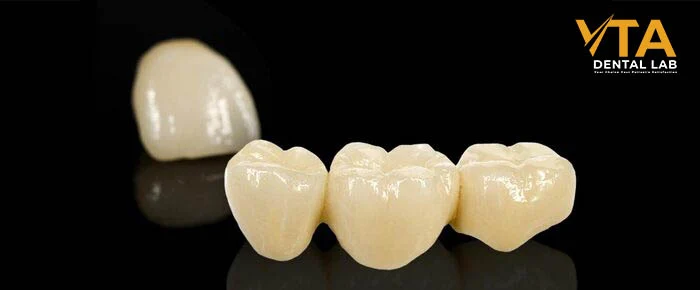
Deep dive into Zirconia crowns
Zirconia crowns represent a perfect blend of strength and aesthetics. These restorations are made from zirconium dioxide—a modern alternative to traditional porcelain crowns. Known for their exceptional durability and strength, zirconia crowns are commonly used in cases that require extra reinforcement, such as molar regions or for patients with bruxism (teeth grinding). The material is highly biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the body and carries minimal risk of allergic reactions.
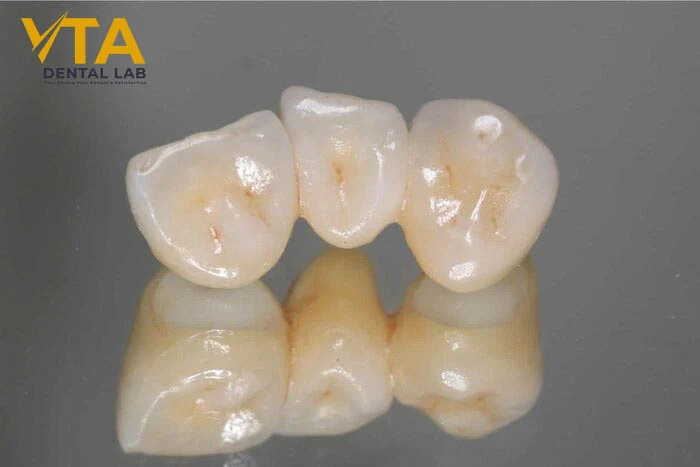
Zirconia crowns are fabricated using advanced CAD/CAM technology, which enables the production of highly precise restorations with a perfect fit and consistent quality. The digital workflow also reduces the time required to create them. Once milled, the crowns are hand-finished by dental technicians to deliver a final restoration that meets the highest standards.
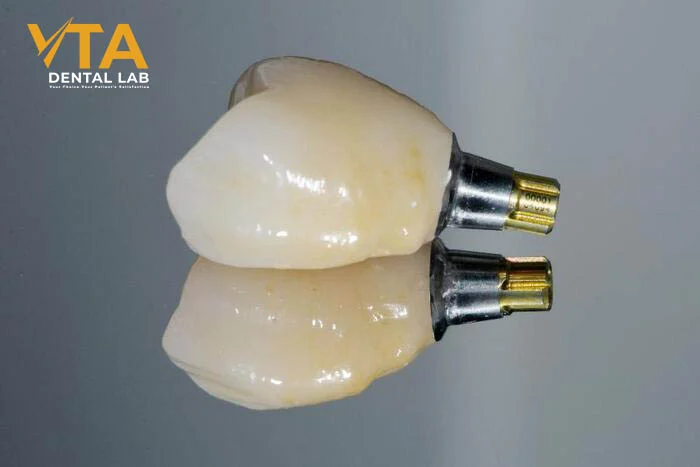
One of the standout features of zirconia crowns is their long-term structural integrity. Unlike porcelain, zirconia is highly fracture-resistant and extremely strong. This makes it ideal for patients with strong bite forces or a history of dental trauma. Despite its superior hardness, zirconia maintains a natural appearance, and restorations can be monolithic or layered with porcelain to achieve a more lifelike result. Notably, advancements in zirconia manufacturing, such as multilayer monolithic zirconia, have significantly improved the material’s translucency, offering esthetics that closely mimic natural teeth.
What Are the Key Differences Between Porcelain Crowns vs Zirconia Crowns?
Benefits of Porcelain Crowns
Porcelain crowns offer several notable benefits, making them a popular choice among patients. One of the most significant advantages is aesthetics. Their natural translucency and excellent shade-matching ability make them an ideal solution for restoring front teeth. Patients can achieve a harmonious and attractive smile, improving overall appearance and boosting confidence.
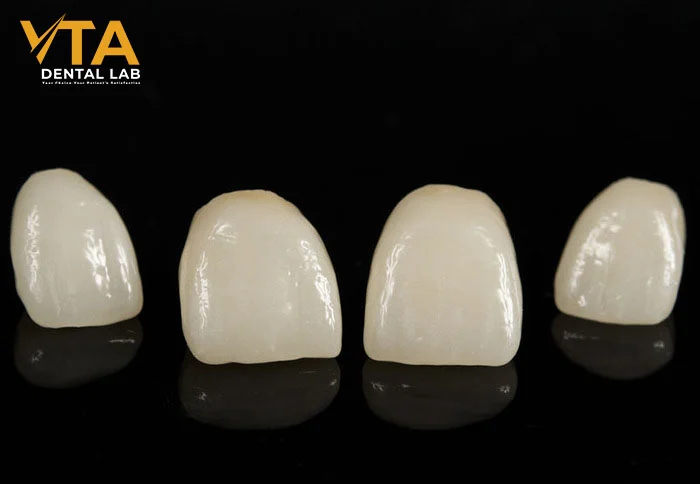
Another thing to consider is that porcelain crowns are highly regarded for their biocompatibility. As a ceramic material, porcelain is generally well-tolerated by the gums and surrounding soft tissues. This reduces the risk of allergic reactions or irritation, making it suitable for patients with sensitive systems. Additionally, the smooth surface of porcelain restorations helps prevent plaque accumulation, contributing to better oral hygiene and reducing bacterial buildup.
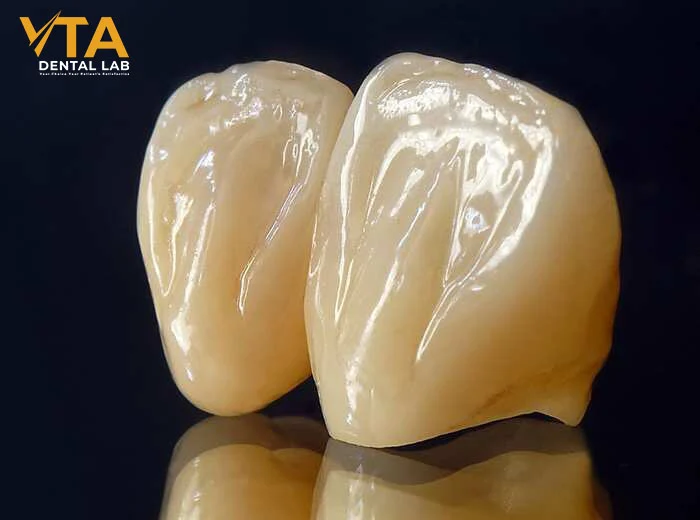
Porcelain crowns are also highly versatile—they can be used in a wide range of clinical situations, including covering discolored or fractured teeth, supporting dental bridges, or serving as final restorations for implants. This versatility makes them a valuable option in restorative dentistry. Moreover, advances in dental technology have led to improvements in the strength and durability of porcelain crowns, allowing them to withstand daily wear while maintaining their natural appearance.
Benefits of Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns offer a range of outstanding benefits that make them a reliable choice for many dental patients. The first is durability. Zirconia is one of the strongest materials used in dental restorations today, providing excellent resistance to chipping and wear while being gentle on opposing teeth. This makes it particularly suitable for patients who grind their teeth or need restorations in posterior regions where bite force is higher.
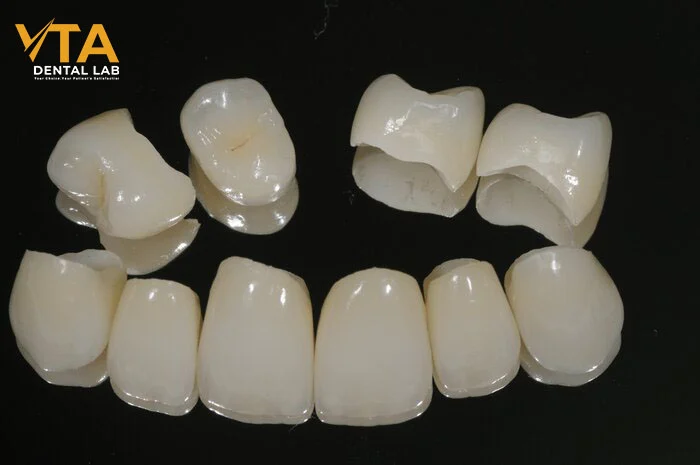
Another key advantage of zirconia crowns is their high biocompatibility. Being metal-free, they carry a very low risk of allergic reactions and are gentle on the gingival tissues—ideal for patients concerned about potential metal sensitivity in dental work. Additionally, the smooth surface of zirconia helps resist plaque accumulation, promoting better overall oral health.
Aesthetic considerations are another strong point of zirconia crowns. Advances in dental materials have led to high-quality zirconia, such as multilayer zirconia, which can closely replicate the shape and appearance of natural teeth. Dental technicians can customize the shade and character of each crown to achieve the most harmonious result, delivering a perfect smile for the patient.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Porcelain Crowns vs Zirconia Crowns
- Strength and Durability
Zirconia crowns are renowned for their exceptional strength and fracture resistance, making them ideal for posterior teeth and patients with bruxism or strong bite forces. While porcelain crowns also offer good durability, they are more prone to chipping and are generally recommended for anterior restorations where occlusal pressure is minimal.
- Aesthetics
Porcelain crowns are superior in translucency and light diffusion, closely mimicking natural enamel. This makes them highly suitable for visible areas like the front teeth. Zirconia, especially in monolithic form, tends to be more opaque. However, advances in multilayer zirconia have significantly enhanced their esthetic appeal, offering lifelike shading and translucency for both anterior and posterior applications.
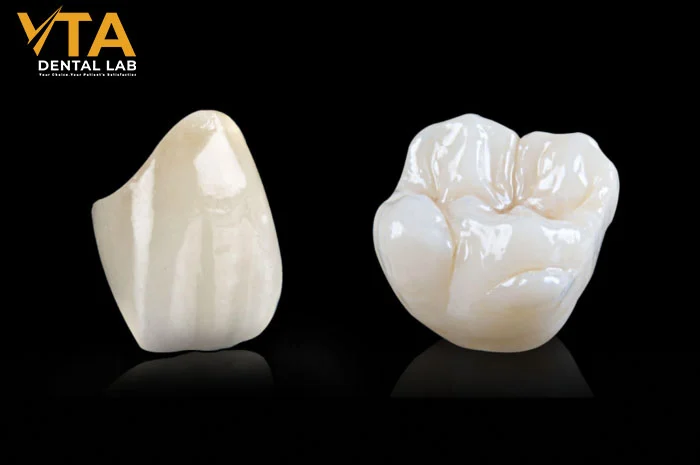
Porcelain crowns vs zirconia crowns comparison showing translucency and durability
- Biocompatibility
Both porcelain and zirconia crowns are highly biocompatible and well-tolerated by soft tissues. Zirconia, being a metal-free ceramic, carries minimal risk of allergic reaction, making it a preferred option for patients with metal sensitivities. Its biologically inert nature also helps reduce soft tissue inflammation and promotes long-term periodontal health.
- Wear on Opposing Teeth
Due to its hardness, zirconia can cause wear on opposing enamel if not properly polished or glazed. Porcelain, though softer, can also be abrasive depending on surface finish. Proper finishing techniques are essential for both materials to minimize wear and maintain occlusal harmony over time.
- Restoration Site and Indication
Zirconia is ideal for posterior crowns, implant-supported restorations, and long-span bridges due to its strength and structural stability. Porcelain is better suited for anterior crowns where aesthetics is paramount. Material selection should be based on both functional requirements and visual expectations of the case.
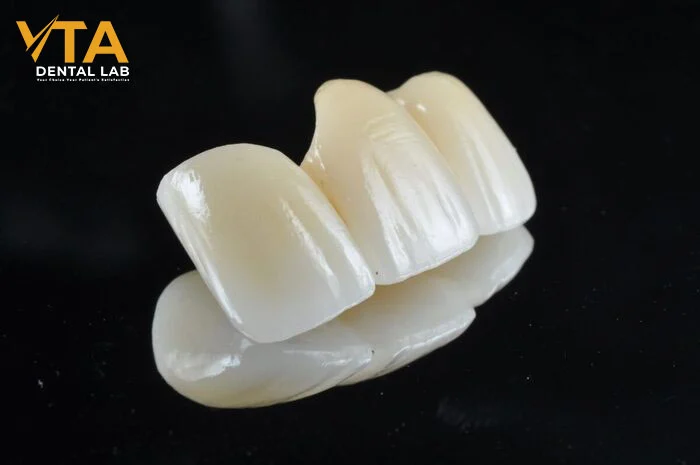

- Fabrication Process
Zirconia crowns are typically milled as monolithic restorations using CAD/CAM technology, allowing for high precision and reduced turnaround time. In contrast, porcelain crowns often involve manual layering over a core, which enables customized shading and more refined aesthetic control, especially important in cosmetic cases.
- Cost
Cost can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the lab work involved. Monolithic zirconia crowns are often more cost-effective due to simplified production. Layered porcelain crowns generally incur higher costs due to the artisanal work required to achieve high aesthetic standards.
Summary
In summary, the decision between porcelain crowns vs zirconia crowns should be based on several factors, including esthetics, durability, cost, and the patient’s clinical needs. Porcelain crowns are an excellent option for patients who prioritize a natural appearance, making them ideal for anterior restorations. Their superior translucency can enhance a patient’s smile, though they may require careful handling due to a higher risk of chipping.
On the other hand, zirconia crowns offer unmatched strength and durability, making them better suited for patients with severe bruxism or restorations in high-stress areas like molars. Advances in digital dental technology allow zirconia crowns to be precisely milled for an accurate fit and lifelike appearance, though they may come at a higher price point.
Importantly, choosing the right dental laboratory plays a critical role in achieving consistent quality and delivering exceptional patient outcomes. VTA is a full-service dental lab trusted by local dental practices across the United States. If you need case support or would like to discuss specific restorations, contact our team today — we’re here to help you deliver the best care to your patients.