Dental implant abutments: Types, Materials, and Benefits
Implant abutments are a critical component in the dental implant process, serving as the connection between the implant fixture and the prosthetic tooth. These small yet essential pieces ensure the stability, functionality, and aesthetics of dental restorations, making them a cornerstone of modern dentistry. In this article, we will explore everything about implant abutments, from their role and materials to proper maintenance for long-term success.
Understanding implant abutments
The implant abutment is a small part but crucial piece in the dental implant that connects the implant post inserted into the jawbone – to the visible tooth replaccment. It acts as a foundation for the artificial crown, enabling the entire implant structure to mimic the natural tooth’s appearance and function.
Implant abutments are typically made from biocompatible materials such as titanium, zirconia, or ceramics, ensuring they integrate seamlessly with surrounding tissues. There are two primary types of implant abutments: stock abutments and custom abutments.
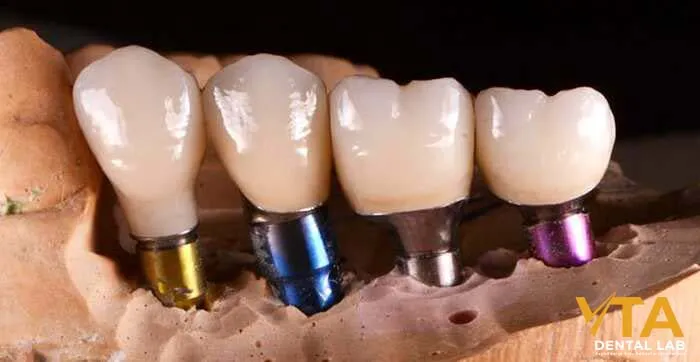
Types of Implant abutments
Stock Abutment
Prefabricated fixed abutments come in a variety of standard shapes and sizes. They are an off-the-shelf option for dental implant restorations, providing a cost-effective and time-saving solution. However, because they are not customized to each patient, there may be a trade-off between fit and esthetics.
Stock abutments are often used in areas with a lot of surrounding soft tissue and where esthetics are less of a concern, such as premolars and molars.

Custom Abutment
Custom dental implants are designed specifically for each patient’s dental details and characteristics using advanced CAD/CAM technology. Therefore, they have a superior fit and aesthetics, especially in complex cases or in highly visible areas such as the front teeth.
Materials of Dental Abutment
Implant abutments are made from various materials, each selected based on specific functional and aesthetic requirements. The most commonly used materials include:
Titanium
Implant abutments made from titanium offer high biocompatibility and are renowned for their strength and durability. They promote osseointegration, ensuring a secure connection with the implant. This material is suitable for both posterior and anterior teeth due to its reliability.
Zirconia
Zirconia is highly regarded for its aesthetics, closely resembling the natural color of teeth, which enhances the overall visual appeal. Additionally, implant abutments made from zirconia offer excellent biocompatibility and resistance to plaque accumulation.

Factors to Consider When Choosing an Abutment
Selecting the appropriate abutment is crucial to the success of the dental implant procedure. Several factors need to be considered, including:
Implant Location: For molars, durability is prioritized, making titanium a popular choice. For anterior teeth, where aesthetics are critical, zirconia abutments are preferred.
Patient’s Anatomy: The unique shape and size of the patient’s mouth influence whether a stock or custom abutment would be more suitable.
Aesthetic Requirements: In cases where the implant is visible, custom zirconia abutments provide a natural and lifelike appearance.
Budget: Custom abutments typically cost more than stock abutments, which may influence the decision based on the patient’s financial considerations.
How Implant Abutments Are Placed
There are two methods for placing the implant abutment onto the implant post:
Delayed Abutment Placement: In this method, the gum tissue is allowed to heal over the abutment, which typically takes about six months. After healing, the dentist makes a small incision in the patient’s gum to expose the implant and create space for the dental crown to be attached.
Use of Healing Abutments: Healing abutments are attached to the outer portion of the implant. These abutments are much wider than the implant post, providing sufficient room for the crown as the surrounding gum tissue heals. Healing caps are often preferred by patients as they eliminate the need for a second surgical procedure.
Once osseointegration is complete, the healing abutment is removed, and the final dental crown is placed securely onto the implant.
Maintenance and Care of Implant Abutments
Proper care of implant abutments is essential to maintain their functionality and longevity:
Daily Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day and use dental floss to prevent plaque buildup around the prosthetic teeth.
Regular Dental Checkups: Schedule routine dental visits for professional cleaning and to monitor the condition of your implants. These visits are crucial for maintaining overall oral health and implant stability.
Avoid Hard Foods: Refrain from eating hard or sticky foods, as they can damage the implant or crown and compromise the dental restoration.
Technological Advancements in Implant Abutments
Modern dental technology has revolutionized implant abutments:
CAD/CAM Technology: Enables precise design and fabrication of custom abutments, ensuring a perfect fit for each patient.
Digital Impressions: Eliminate the need for traditional molds, making the process more comfortable and accurate.
Material Innovations: Zirconia material offers improved durability and natural aesthetics, especially for visible teeth

Conclusion
The implant abutment plays a vital role in the success and durability of a dental implant. It is not only the connecting element between the implant and the crown but also influences the overall health of the surrounding gum tissue and the process of osseointegration.
VTA Dental Lab, a full-service dental laboratory in the USA, leverages advanced technology and the skilled craftsmanship of our expert technicians. We are dedicated to providing high-quality, customized products tailored to the unique needs and conditions of each patient, helping you deliver perfect smiles to your patients.