Cementing Zirconia Crowns: Decision The Success Of The Workflow
Cementing Zirconia Crowns requires more complex techniques and preparation compared to PFM crowns, although Zirconia crowns have decisively surpassed the dominance of PFM crowns to become the most popular choice in dental restorations today, thanks to their ease of use, durability, and aesthetics.
Due to their remarkable development and wide-ranging applications, tens of millions of zirconia crowns have been delivered to dentists over the years and also led to the development of various types of materials, including solid and layered zirconia.
With a product that is becoming increasingly popular like Zirconia Crowns, achieving optimal results, improving patient outcomes, and mastering the steps for Cementing Zirconia Crowns is crucial, especially with the decision that determines the success of the workflow: Cementing Zirconia Crowns.
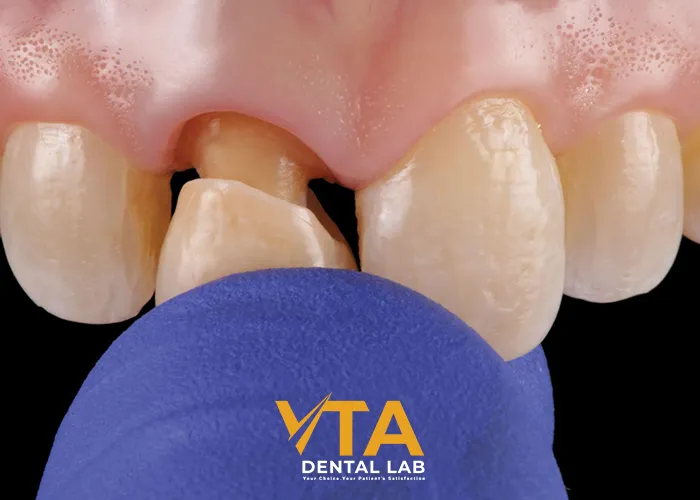
The Types Of Materials Commonly Used For Cementing Zirconia Crowns
Resin-modified glass Ionomer (RMGI)
Resin-modified glass Ionomer (RMGI) is a hybrid material that combines the best features of Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) and Resin-Based Composite (RBC). It is less irritating to soft tissues and safe for human health. This material is suitable for various types of cementing restorations including Cementing Zirconia Crowns due to its excellent adhesion, tack cure time, ease of use, and faster cleanup.
Like other glass ionomer types, RMGI has fluoride-releasing properties that help protect and strengthen tooth enamel by resisting acid attacks and preventing cavities. Its color, which closely matches natural teeth, and its good mechanical strength also contribute to achieving optimal aesthetics and durability for zirconia crowns. These cements are ideal for zirconia cases with retentive preparations but offer limited adhesive properties for non-retentive preparations.
Resin-modified glass Ionomer (RMGI)
Adhesive resin cement
Adhesive resin cement is a type of cement with the main component being resin, combined with additives to create a strong adhesive layer between the restoration and the natural tooth. This provides the strongest retention but is highly sensitive to technique, requiring precision and meticulousness during application, as even minor errors can affect the quality of the restoration.
These cements also have color stability similar to RMGI, along with excellent water resistance. However, due to the high technical demands, they are less commonly used than RMGI and are ideal only for veneer cases and non-retentive zirconia restorations.

Adhesive resin cement
Self-adhesive resin cement
Self-adhesive resin cement is a type of cement that combines the properties of resin with self-adhesive capabilities, eliminating the need for primer systems or additional bonding agents. It offers a more convenient solution compared to the two aforementioned options, as it does not require complex surface preparation, is easier to handle, and demands less technical skill while still providing strong adhesion. However, its high cost and limited compatibility for certain cases mean it is not as widely used as RMGI.
Self-adhesive resin cement
The Steps Of The Cementing For Zirconia Crowns
-
Preparing The Crown
After try-in, all Zirconia Crown must be decontaminated (through air abrasion, zirconia cleaning solutions, and hydrofluoric acid) to avoid contamination from phosphates in saliva, which have a strong affinity for zirconia and can cause chemical reactions that hinder adhesion. Next, sandblast the internal surface of the crown with aluminum oxide at a pressure of 2.5 bar to remove any residues and create a roughened surface to enhance adhesion. Then, clean the restoration with steam and allow it to dry completely before cementation.
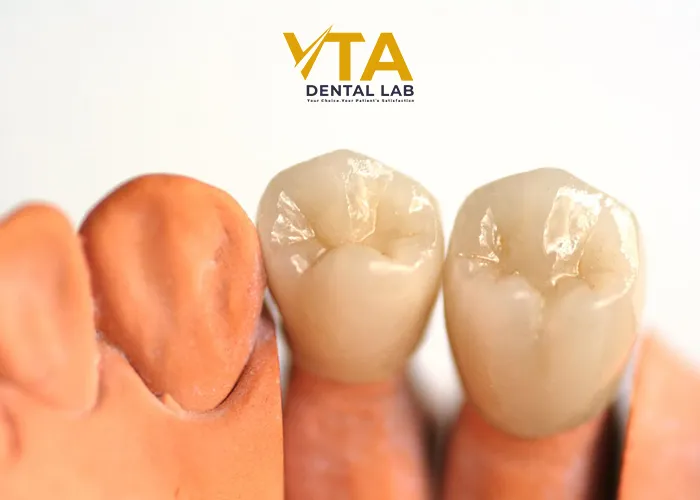
Preparing The Crown
-
Pretreating The Tooth
After removing the temporary crown, it is essential to clean off all residues from temporary cement, desensitizing agents, hemostatic agents, and disinfectants to ensure the best possible conditions for adhesion. Mechanical cleaning with pumice powder will be effective for this purpose.
-
Apply Cement And Seat The Crown
Dispense a small amount of cement onto a mixing pad to ensure the mixture is thoroughly blended, achieving the proper consistency for easy handling and application. Next, apply the cement directly to the internal surface of the zirconia crown. Press the crown firmly into place with your finger, ensuring that all areas in contact with the tooth are covered until the crown is securely bonded to the tooth.
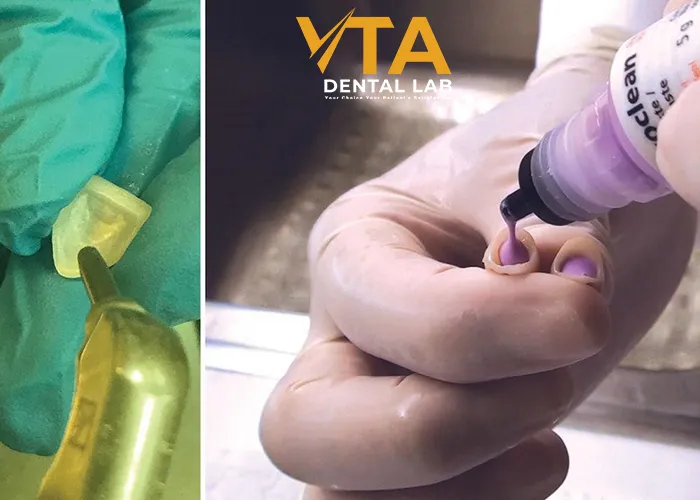
Apply Cement And Seat The Crown
-
Clean Up
Tack the cure for 1-2 seconds. Stay within the recommended tack cure time, otherwise, clean-up will be extremely difficult. For a controlled curing time, use an LED curing light. Finally, remove the excess cement with a scaler while holding the crown in place. Light cure the tooth for 20 seconds per surface or wait 6 minutes from the start of the mix for a dark cure. Finish and polish the restoration as needed.
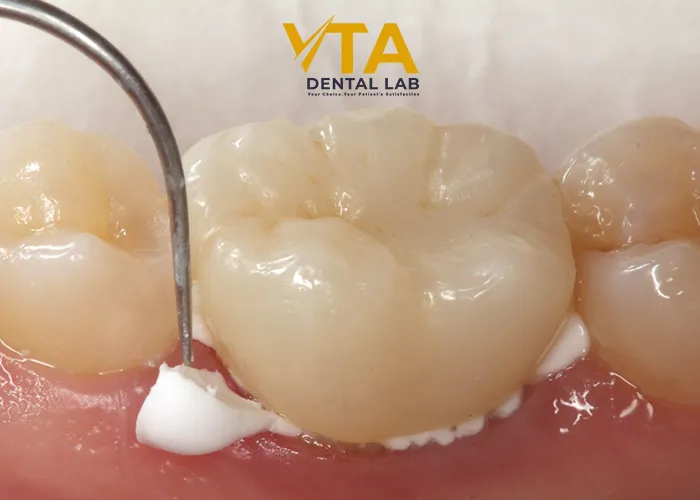
Clean Up
Summary
Typically, Cementing Zirconia Crowns is performed by the Dr. at the dental clinic. However, for some cases of Implant Crowns, this step is carried out at the laboratory after the crowns have been fully fabricated. For over 20 years, VTA has been a laboratory specializing in Fabricating and Cementing Zirconia Crowns for millions of implant cases for clients from the USA, Singapore, Japan, and various European Union countries. We understand that elevating your practice comes not only from the overall work but also from detailed steps like Cementing Zirconia Crowns.
When you come to VTA, you can be assured that our team of technicians will pay careful attention to every detail of your workflow. Please contact us via email: ca@vtadentallab.com or az@vtadentallab.com